The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted an unprecedented crisis in California child care.
In May 2020, the Center for the Study of Child Care Employment (CSCCE) released results from a survey of more than 2,000 child care programs throughout California, painting a grim picture of the devastating impact of COVID-19. Two months later, as the state began to reopen its economy, we conducted a follow-up survey with those same respondents to understand the changing nature of California child care. 953 programs responded to this survey from June 22 to July 1, 2020: 40% of respondents were center-based administrators, and 60 percent were home-based family child care (FCC) providers.
This data snapshot highlights the key findings from our survey results along with responses from providers in their own words. The results show that the attempt to reopen the economy has only escalated the crisis in California child care, exposing providers to the dual threats of health risk and the potential collapse of their programs.
Key Findings
- Child care providers and early educators are deeply concerned about the health risks of operating during the pandemic.
- The reopening process has introduced new financial challenges for programs.
- Decreased capacity and increased costs are disrupting an already financially unstable industry.
- Without more public funding, the California child care industry will continue to collapse.
Child care providers face serious health risks.
Health risk emerged as a primary reason for program closure, especially among family child care providers.
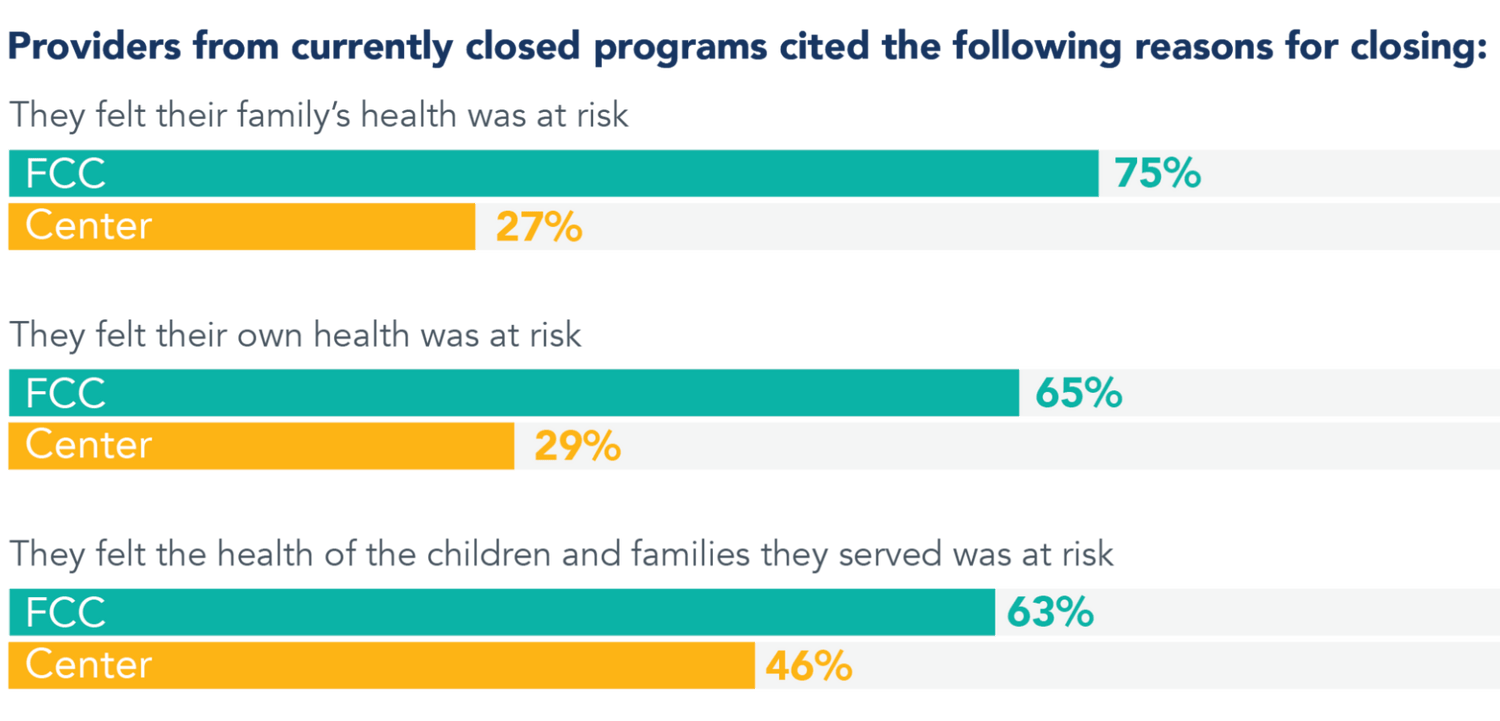
Health and safety continue to be major concerns for all programs, whether they are currently open or closed but considering reopening.
- 38% of providers are worried that they will be exposed to COVID-19 by the children/families they serve.
- 38% of providers are worried that they will expose their own families to COVID-19 by having their program open.
- 36% of providers are worried that their staff will be exposed to COVID-19 by the children/families they serve.
- 29% of providers are worried that children will be exposed to COVID-19 while attending their program.
Providers speak: “The pressure to open is extreme.”
“The pressure from the community to open is extreme, and there seems to be very little concern on the part of the parents for the health of the staff and/or the older members of their own families.”
“Now that my child care is open again, it is nerve-wracking knowing that I can get infected and potentially cause harm to the kids in my program or my family.”
Providers grapple with decreased capacity, reduced income, and higher costs.
Open programs are operating with decreased capacity and reduced attendance, resulting in loss of income.
- 77% of open programs have experienced loss of income from families.
- 99% of open centers and 78% of open FCC programs have fewer children attending than before the pandemic (January 2020).
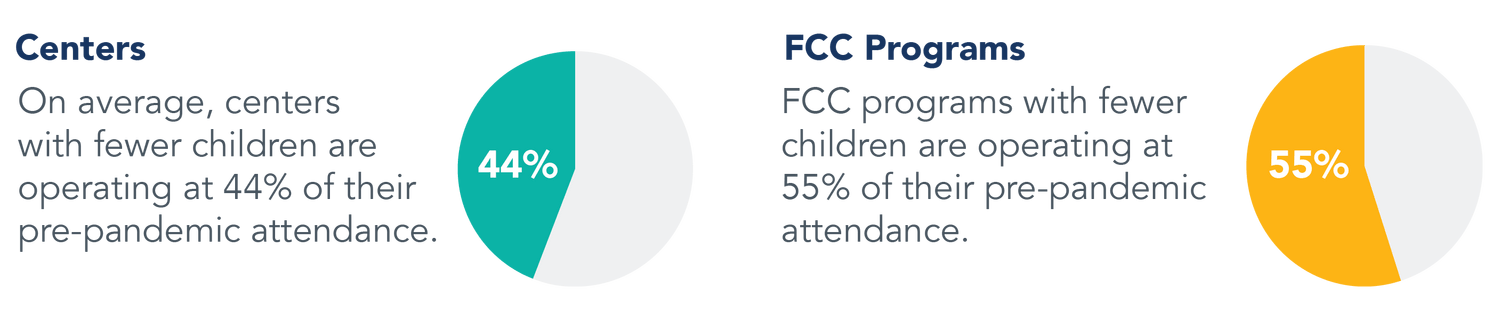
More robust cleaning and safety requirements have led to higher operating costs for open programs.

Providers speak: “Without government subsidies, we won’t survive.”
“There is no way we will survive financially with the limited group size. We had 150+ students. Now the most we can have is 48. Parents can’t possibly pay enough to cover our costs. Without government subsidies, we won’t survive.”
“The guidelines are not in line with a sustainable business. We were already barely financially stable, and now we are absolutely not. Our rates would have to double or triple.”
“The cleaning guidelines and requirements for supplies will be taxing for our school…. Our overhead will certainly go up while our income will go down.”
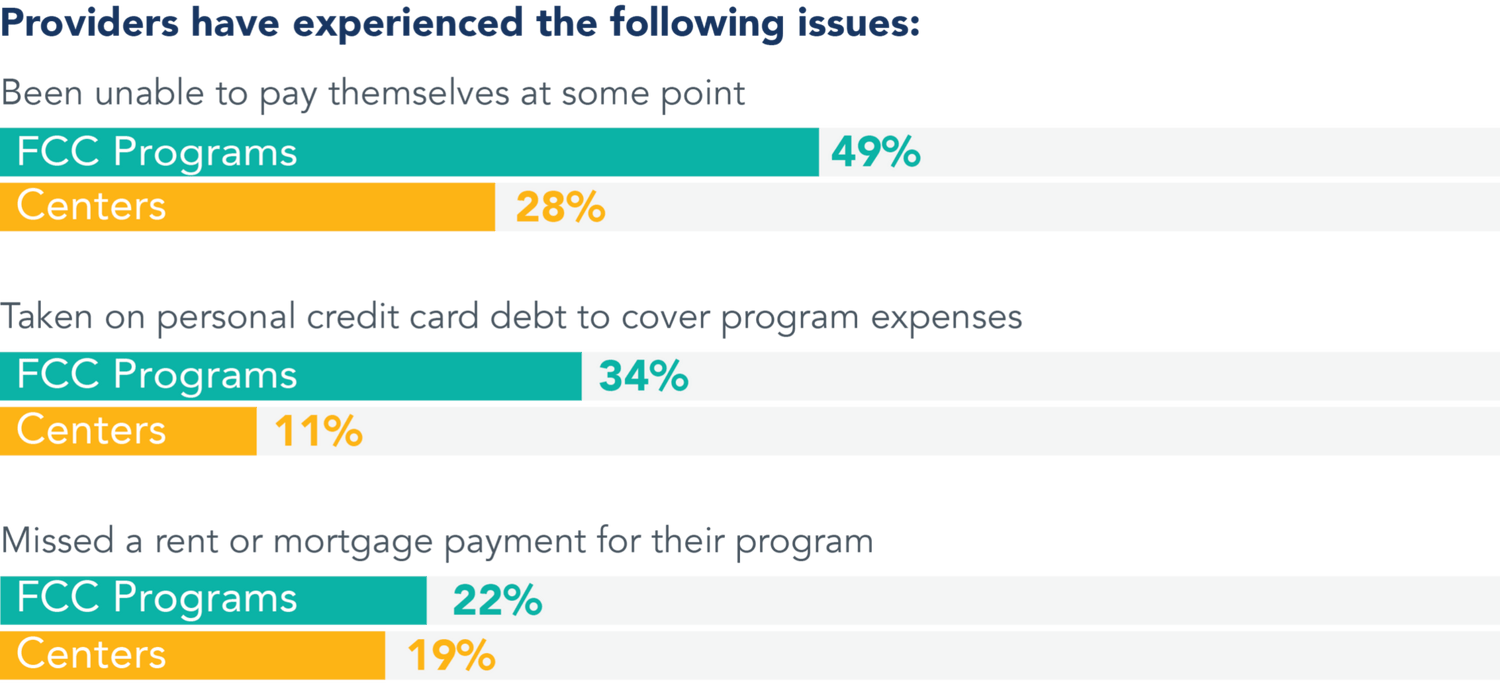
Without public funding, providers’ financial health is increasingly dire.
Many providers cannot afford to close.
- 80% of open programs reported that they are open because they lack the financial resources to survive a closure.
Providers are struggling to understand and adhere to new guidelines and regulations.
Social distancing is not feasible or practical with young children.
- 27% of all programs think the guidelines for social distancing are not clear
- 34% of all programs say they cannot adhere to the social distancing guidelines.
Programs need more concrete guidelines.
- 45% of all providers say they need additional guidance or resources on regulatory changes.
Providers speak: Conflicting, unrealistic guidelines.
“We are doing the best we can with all the conflicting guidelines, mandates, and regulations. Too much is left to interpretation. The line between the state and local directives is blurred and confusing.”
“I wish that agencies would collaborate together in a more seamless fashion so that we in the trenches do not get conflicting information…. Some of the regulations coming out are obviously from folks who have never worked with young children!”
“We are unable to comply with the guidelines realistically. There is no social distancing for 2- and 3-year-olds, nor mask wearing, nor containing body fluids. If we want safe childcare for families through this, we need financial help keeping lower ratios than we currently have.”
Open programs continue to have difficulty obtaining and paying for essential health and safety supplies.
During the past month:
- 38% of open programs have not had sufficient PPE or cleaning/sanitizing supplies.
- 10% of open programs did not have sufficient food for their program.
Looking ahead to the next month:
- 37% of open programs do not have enough funds to pay for the PPE or cleaning/sanitizing supplies they need.
- 20% of open programs do not have enough funds to pay for the food they need.
Providers speak: A “nightmare” finding sanitizing supplies.
“Not being able to find sanitizing and disinfecting supplies has been a nightmare. I want to continue to support the community, but in order to do that I need to be supported, as well.”
“Getting supplies is a challenge. It’s expensive to buy a no-touch thermometer, gloves, sanitizing supplies, disposable towels for the bathrooms, hand sanitizer, etc.”
“I can’t believe that everyday before and after work I have to search for cleaning supplies!”
The pandemic has worsened an already widespread teacher shortage.
Many center-based staff cannot work or are concerned about health risks.
- 62% of open centers have staff who are not working due to concerns about the health risks.
- 48% of open centers have staff who are unable to work because they are taking care of their own children.
- 35% of open centers have staff who are taking a leave of absence.
On top of the health risks, many staff do not receive employer sponsored health benefits.
- 70% of open centers are not able to provide health benefits for all of their teaching staff.
Programs have fewer paid teachers on staff, due to layoffs, furloughs, and/or staffing shortages.
- 78% of open centers and 61% of open FCC programs have fewer paid teachers now than before the pandemic (January 2020).
Providers speak: “None of my staff wanted to return.”
“We do not want to be frontline workers! Our staff is frightened, and half do not want to return until there is a vaccine.”
“I had to permanently close—none of my staff wanted to return, only one parent wanted to return, my landlord was completely unsympathetic, [and I] can’t meet financial minimums with allowable group sizes.”
Acknowledgements
The California COVID-19 Impact Study is currently supported by grants from the Heising-Simons Foundation, the David and Lucile Packard Foundation, and the TRIO Foundation.
Thank you to Holly Gold and Yohana Quiroz for providing input on early versions of our survey questions.